Now let's draw a mirror image of our triangle Next, we can label the length of the new side opposite 30º "a," and About Triangle A triangle is a unique right triangle whose angles are 30º, 60º, and 90º The triangle is unique because its side sizes are always in the proportion of 1 √ 32 Any triangle of the kind can be fixed without applying longstep approaches such as the Pythagorean Theorem and trigonometric featuresThis allows us to find the ratio between each side of the triangle by using the Pythagorean theorem Check it out below!

Right S And Trigonometry 7 Pythagorean Theorem The Determine Right Triangles 6 Pythagorean Theorem Solve Sides 5 Wp Pythagorean Theorem 4 Special Right Ppt Download
Pythagorean theorem 30 60 90 triangle
Pythagorean theorem 30 60 90 triangle-Now take away the triangle on the right, leaving only the one on the left Now you have a 30°60°90° right triangle Use the Pythagorean theorem to calculate its altitude So the length of the altitude is Now memorize the way this right triangle looks and the lengths of the three sides For you will need it to find the exact values for the Let's walk through exactly how the triangle theorem works and prove why these side lengths will always be consistent With the special triangle ratios, you can figure out missing triangle heights or leg lengths (without having to use the Pythagorean theorem), find the area of a triangle by using missing height or base length information, and quickly calculate
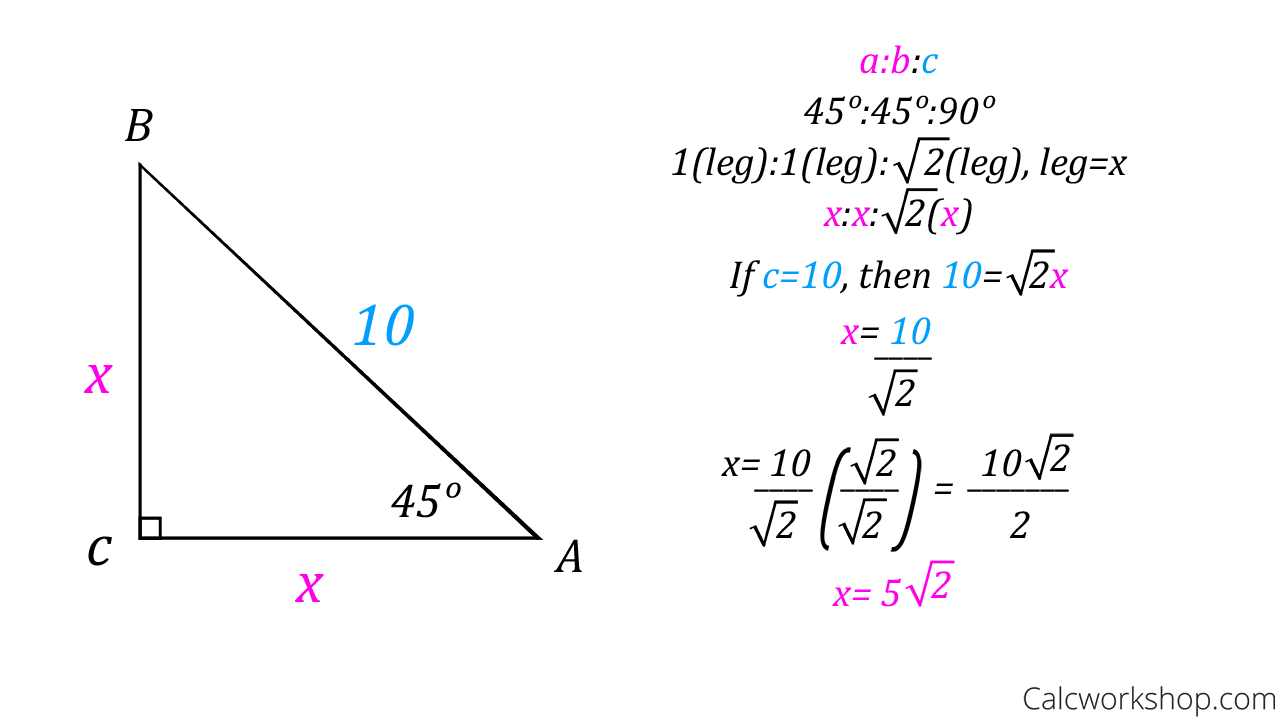



Special Right Triangles Fully Explained W 19 Examples
Pythagoras Theorem Class 10 Chapter 2 Part 1 Pythagorean Theorem 30 60 90 TriangleTopics covered in this 10th Maths video are as follows 1) Theorem On 30Once again, we know that all triangles are similar, so this pattern works for all triangles This pattern has two parts * The short leg is half the length of the hypotenuse * If you know the short leg of the triangle, then multiply the short leg by 3 to get the longer leg The pattern works both ways Draw an equilateral triangle all sides are equal and the angles are all 60 deg From any angle drop a line perpendicular to the base(an altitude) By triangle congruence laws you can prove the 2 resulting triangles are congruent which means the al
A triangle is a right triangle where the three interior angles measure 30 °, 60 °, and 90 ° Right triangles with interior angles are known as special right triangles Special triangles in geometry because of the powerful relationships thatLet's take a look at the Pythagorean theorem being applied to a 30 60 90 triangle Remember that the Pythagorean theorem is a 2 b 2 = c 2 Using a short leg length of 1, long leg length of 2, and hypotenuse length of √3, the Pythagorean theorem is applied and gives us 1 2 (√3) 2 = 2 2, 4 = 4 The theorem holds true with the side Thanks to this 30 60 90 triangle calculator you find out that shorter leg is 635 in because a = b√3/3 = 11in * √3/3 ~ 635 in hypotenuse is equal to 127 in because c = 2b√3/3 = 2a ~ 127 in area is 349 in² it's the result of multiplying the legs length and dividing by
This is an isosceles right triangleThis formula is known as the Pythagorean Theorem Special Triangles Isosceles and Calculator This calculator performs either of 2 items 1) If you are given a right triangle, the calculator will determine the missing 2 sides Here you can enter two known sides or angles and calculate unknown side ,angle or area Special Right Triangles A right triangle with a 30° anglePythagoras Theorem On 30 60 90 Triangle SSC Standard 10 Maths
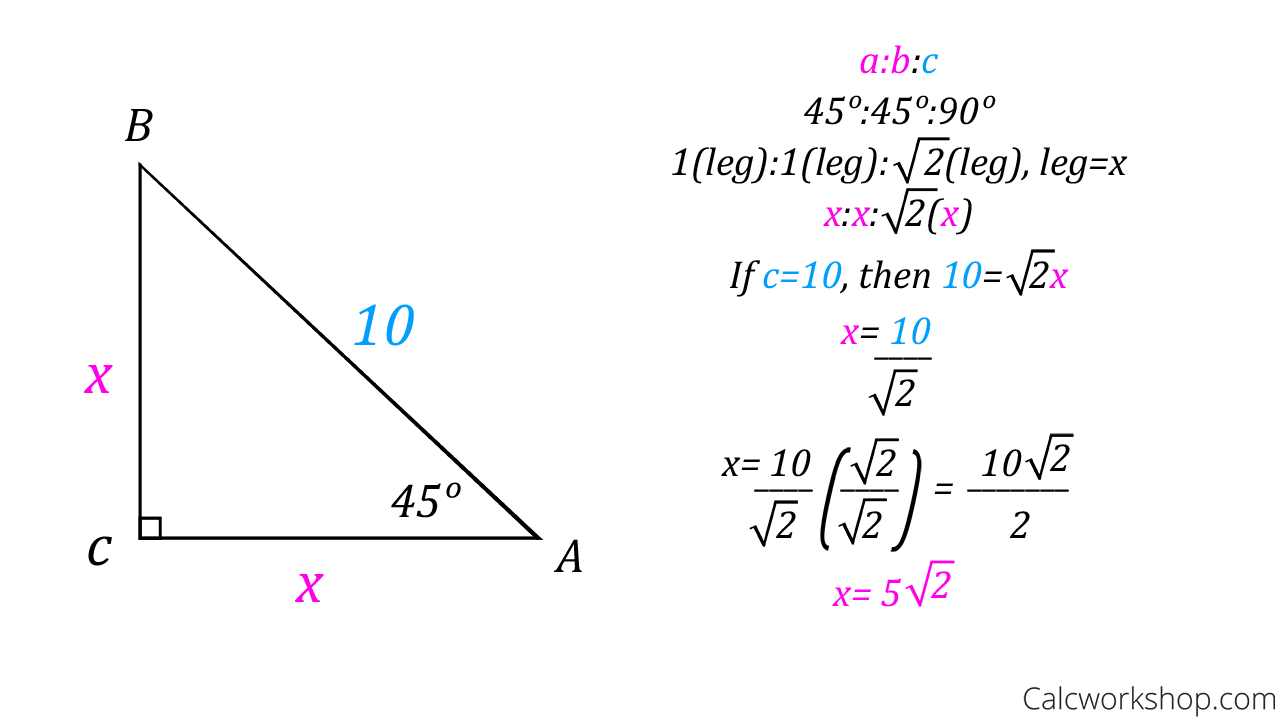



Special Right Triangles Fully Explained W 19 Examples
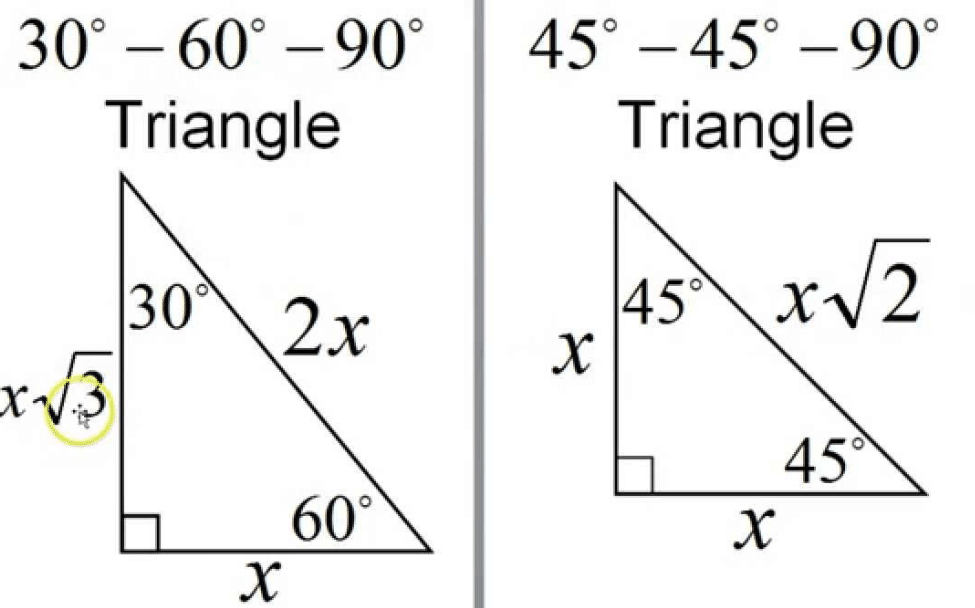



How To Work With 30 60 90 Degree Triangles Education Is Around
Triangles Finding the hyypotenuse triangles triangles help you find the side lengths using equilaterals A is half of an equilateral So if you know the side lengths of the equilateral, it will be simple First, if you know the side length of c squared, then you just need to split it in half to find b squared This is because equilaterals have all the samePythagoras' theorem only works for rightangled triangles, so you can use it to test whether a triangle has a right angle or not Can sin be applied to non right triangles?Chapter 8 Pythagorean Theorem, Triangles, Triangles, Trigonometry STUDY Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity Created by Sierra_Mariduena Terms in this set (10) Pythagorean Theorem If a triangle is a right triangle, then the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs is equal to the square of the length of the hypotenuse



How To Work With 30 60 90 And 45 45 90 Degree Triangles Dummies




Special Right Triangles Fully Explained W 19 Examples
Check out this tutorial to learn about triangles!To play this quiz, please Any triangle of the form can be solved without applying longstep methods such as the Pythagorean Theorem and trigonometric functions Are all isosceles triangles 30 60 90?



Is A 3 4 5 Triangle Also A 30 60 90 Triangle Quora
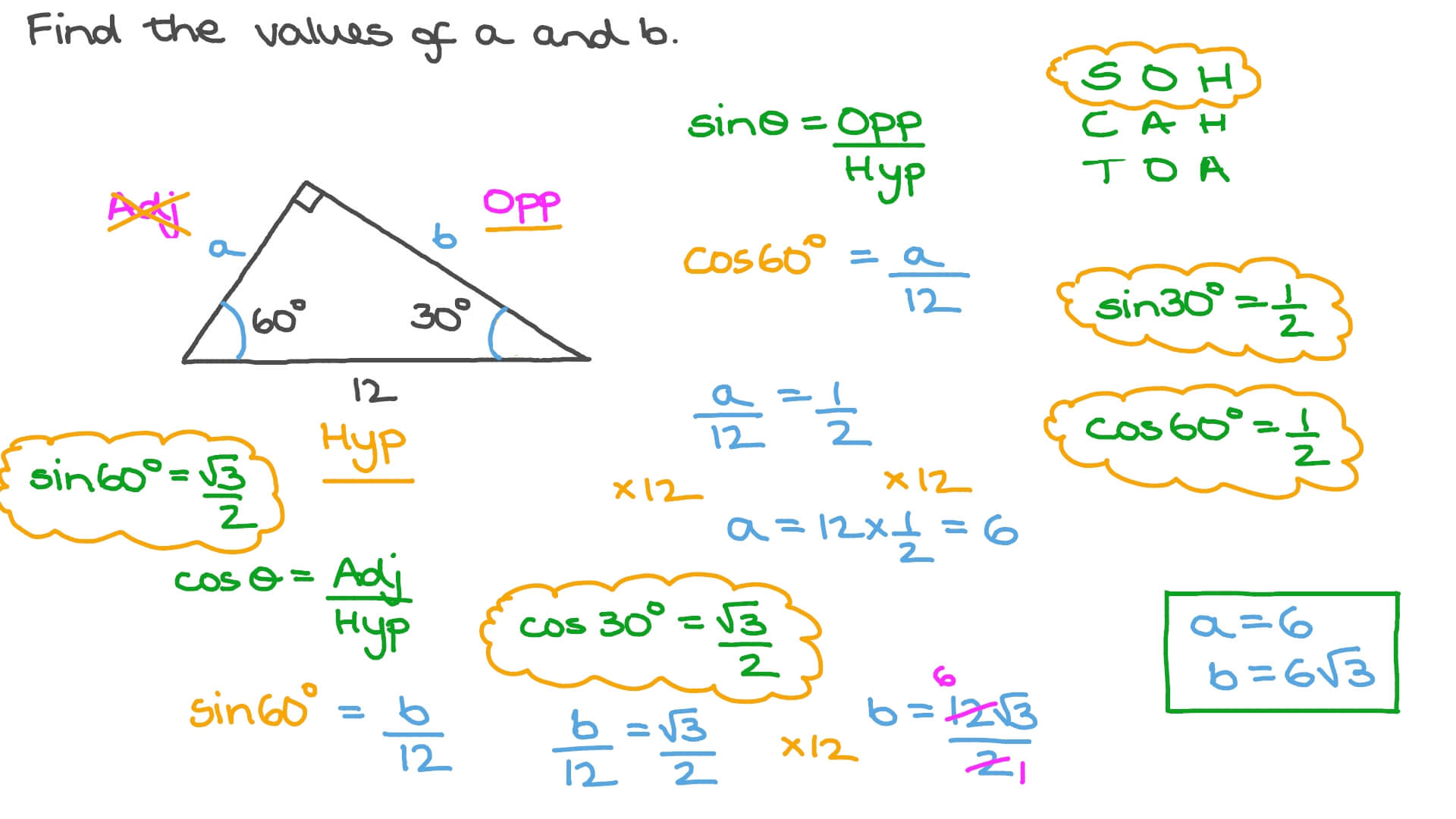



Question Video The Side Lengths Of 30 60 90 Triangles Nagwa
Answer (1 of 8) I ll suggest you to know some trigonometry basics For 30 60 90 The side opposite to 90° ll always be the bigger one, followed by opposite to 60•Use the Pythagorean Theorem to write an equation involving h •Solve the equation for h 3Draw the triangle in as many orientations as possible, keeping the legs either horizontal or vertical (Hint You can rotate and reflect the triangle) 4Draw the triangle in as many orientations as possible, keeping the legs either horizontal or vertical Created Date 9/2/14 10Right Triangles, Pythagorean Theorem and , DRAFT 10th 11th grade 30 times Mathematics 67% average accuracy 2 years ago ahuizenga227 0 Save Edit Edit Right Triangles, Pythagorean Theorem and , 45



1
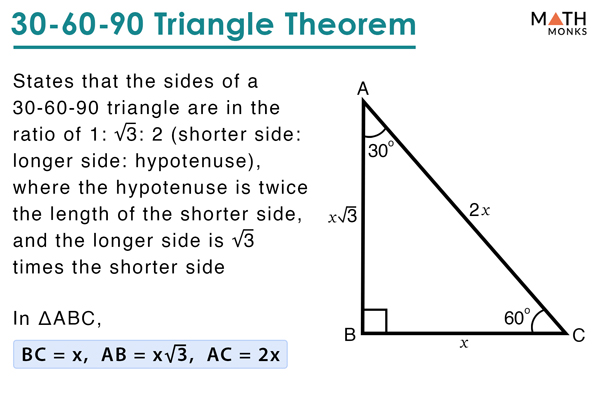



30 60 90 Triangle Definition Formulas Examples
Right Triangles And Pythagorean Theorem The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the legs The hypotenuse is the longest side of a right triangle It is always across from the right angle sed on this right triangle, you can write an equation using the Pythagorean Theorem as followsAlthough all right triangles have special features – trigonometric functions and the Pythagorean theorem The most frequently studied right triangles, the special right triangles, are the 30, 60, 90 Triangles followed by the 45, 45, 90 trianglesThe Law of Sines can be used to
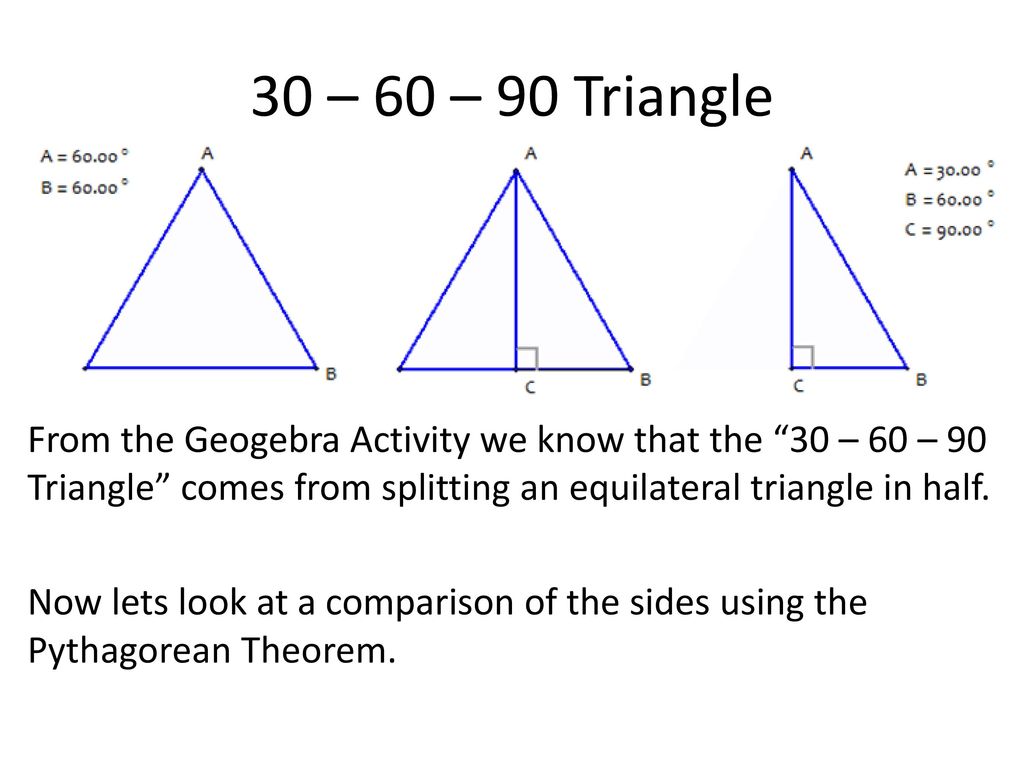



Special Right Triangles Ppt Download
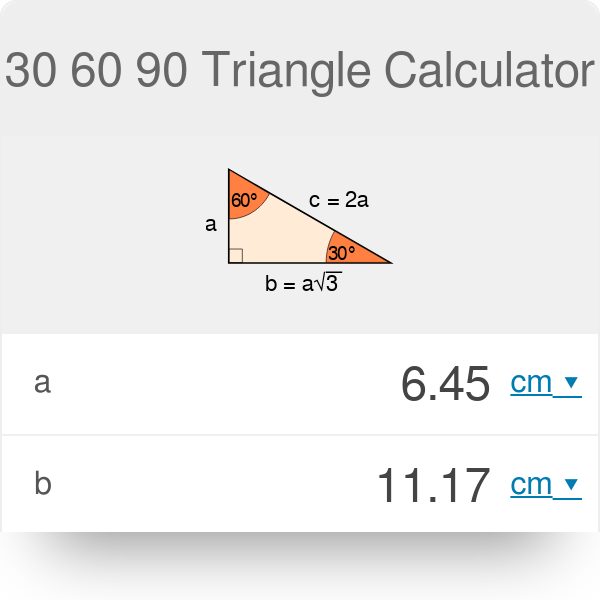



30 60 90 Triangle Calculator Formula Rules
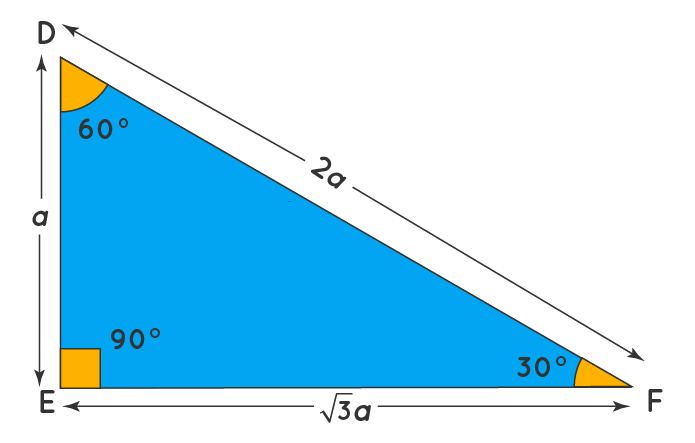
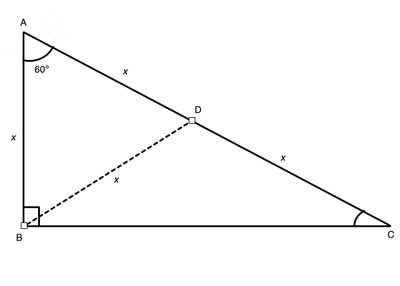
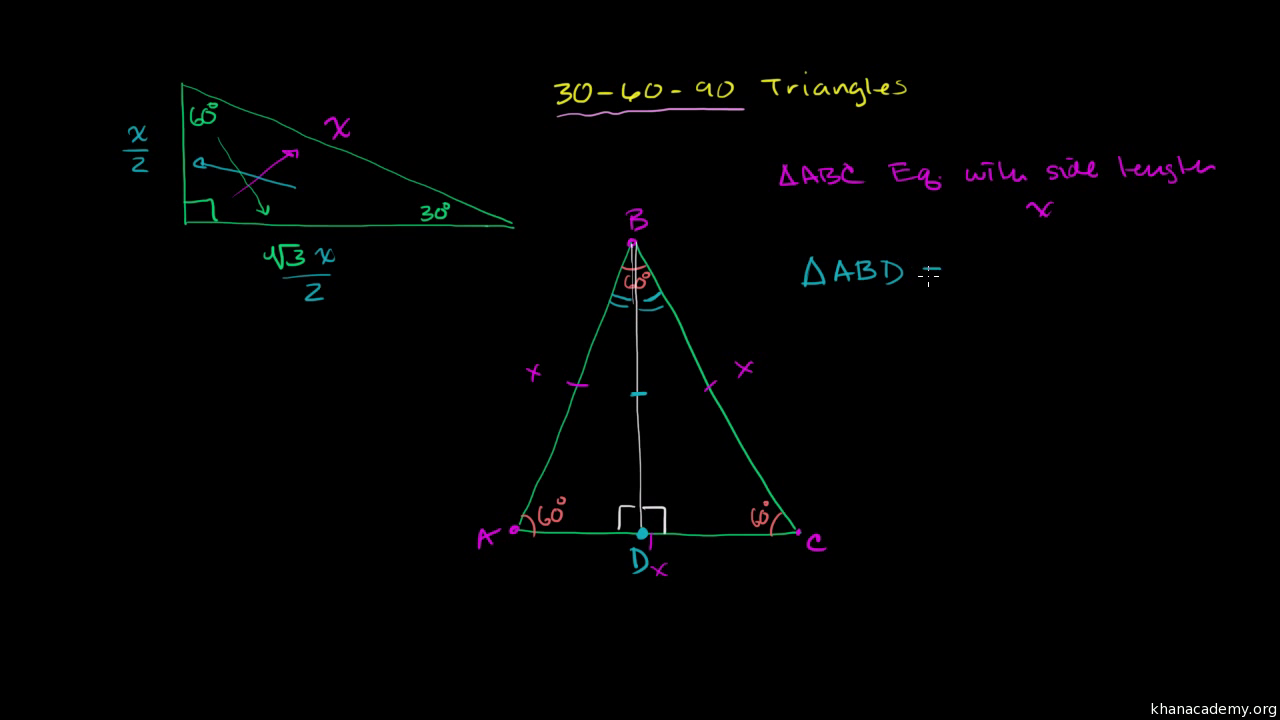
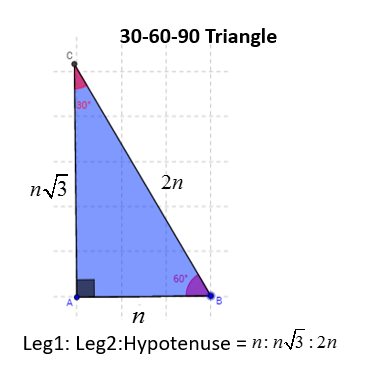
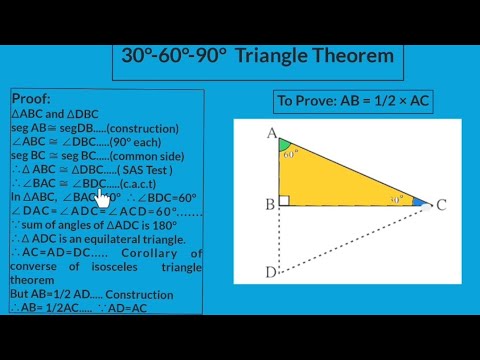
Host a game Live Game Live Homework Solo Practice Practice Play Share practice link Finish Editing This quiz is incomplete!Then ABD is a 30°–60°–90° triangle with hypotenuse of length 2, and base BD of length 1 The fact that the remaining leg AD has length √ 3 follows immediately from the Pythagorean theorem The 30°–60°–90° triangle is the only right triangle whose angles are in an arithmetic progression The proof of this fact is simple and follows on from the fact that if α, α δ, α 2δ The sides of a right triangle lie in the ratio 1√32 The side lengths and angle measurements of a right triangle Credit Public Domain We can see why these relations should hold by plugging in the above values into the Pythagorean theorem a2 b2 = c2 a2 ( a √3) 2 = (2 a) 2 a2 3 a2 = 4 a2




Right S And Trigonometry 7 Pythagorean Theorem The Determine Right Triangles 6 Pythagorean Theorem Solve Sides 5 Wp Pythagorean Theorem 4 Special Right Ppt Download



Special Right Triangles Proof
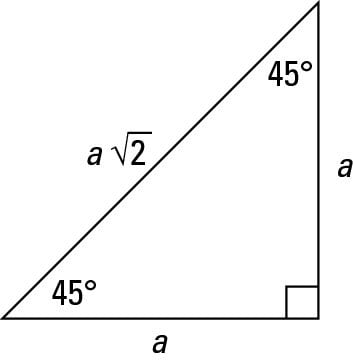
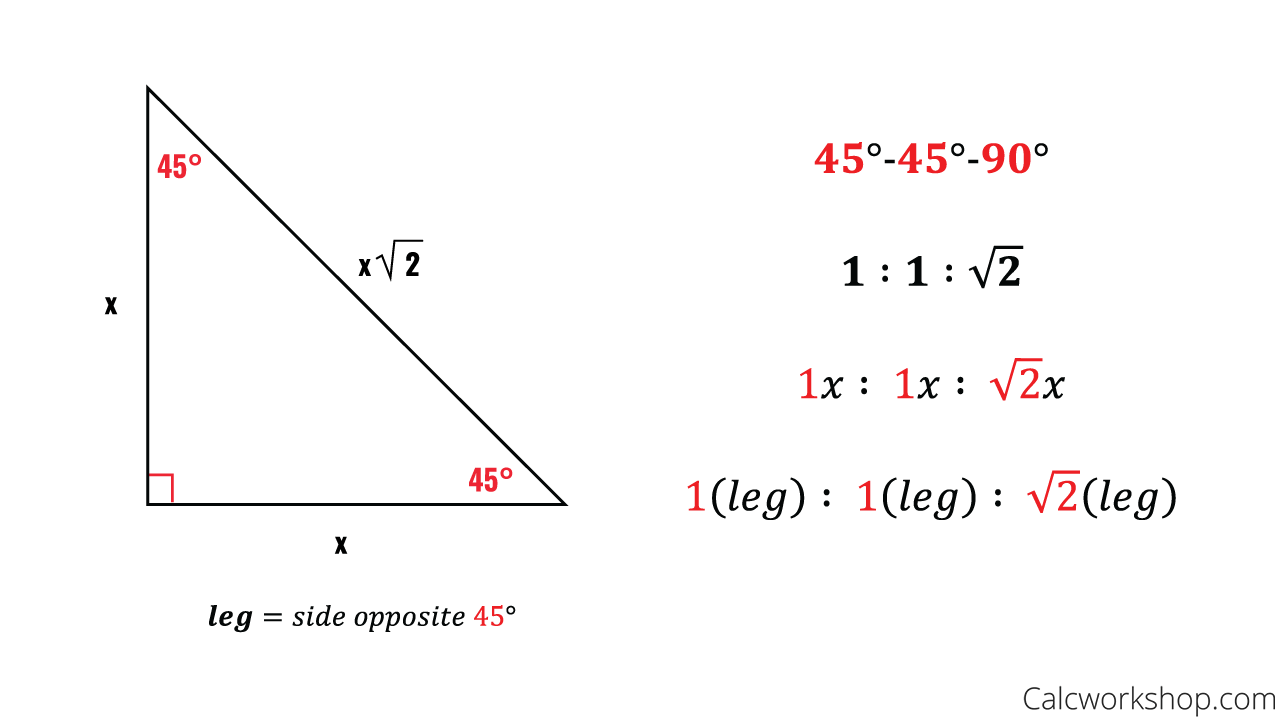
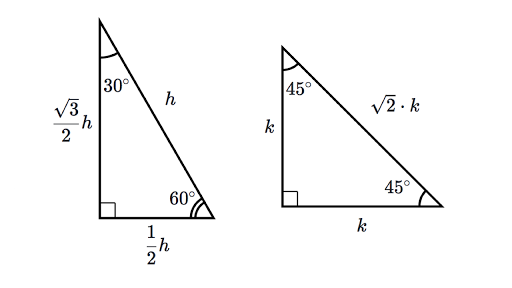
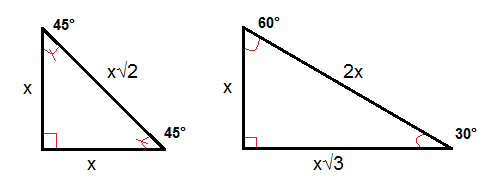
One of the best known mathematical formulas is Pythagorean Theorem, which provides us with the relationship between the sides in a right triangle A right triangle consists of two legs and a hypotenuse The two legs meet at a 90° angle and the hypotenuse is the longest side of the right triangle and is the side opposite the right angle The Pythagorean Theorem tells us that theThe 45°45°90° triangle, also referred to as an isosceles right triangle, since it has two sides of equal lengths, is a right triangle in which the sides corresponding to the angles, 45°45°90°, follow a ratio of 11√ 2 Like the 30°60°90° triangle, knowing one side length allows you to determine the lengths of the other sides of a 45°45°90° triangle This problem can also be solved using trigonometric functions or even revisiting triangle rules What can the Pythagorean Theorem be used for any triangle?



45 45 90 And 30 60 90 Triangles Zona Land Education



Special Right Triangle 30 60 90 Mathbitsnotebook Geo Ccss Math
The Pythagorean Theorem, a2b2=c2, a 2 b 2 = c 2 , can be used to find the length of any side of a right triangle60˜ 6 30˜ T U V 60˜ 30˜ 9˚3 EXAMPLE 4 Explore the Side Lengths of a 30°60°90°a Trnegi l Using an equilateral triangle, show how the lengths of the short leg, the long leg, and the hypotenuse of a 30°60°90° triangle are related 60˜ 30˜ 30˜ 60˜ A C D B Look at ADB Let the length of the short leg ‾AD be s The longer leg must, therefore, be opposite the 60° angle and measure 6 * √3, or 6√3 We can see that this must be a triangle because we are told that this is a right triangle with one given measurement, 30° The unmarked angle must then be 60° Since 18 is the measure opposite the 60° angle, it must be equal to x√3




Special Right Triangles Gmatsyllabus Com




30 60 90 Triangle Theorem Ratio Formula Video
Triangles The Pythagorean T heorem applies to isosceles triangles with a right angle The equation for this triangle is a2b2=c2 In an isosceles right triangle the length of the hypotenuse is the length of the leg times square root of 2 By halfing an equilateral triangle we get two right triangles These type of triangles have a special properties the shortRight Triangles, Pythagorean Theorem and , DRAFT 2 years ago by peggyrenier Played times 0 10th 11th grade Mathematics 70% average accuracy 0 Save Edit Edit Print;Students are familiar with the ratios of the sides of special right triangles with angle measures 45–45–90 and 30–60–90 Prove the Pythagorean Theorem Using Similarity Classwork Exercises 1–3 Simplify as much as possible Find the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle whose legs have lengths 50 and 100
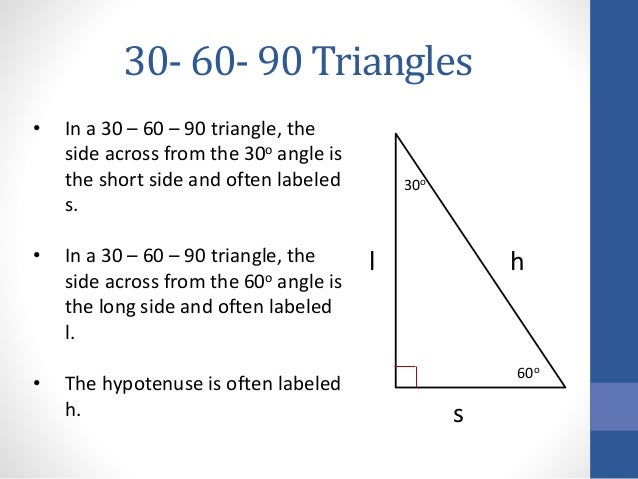



30 60 90 Triangles
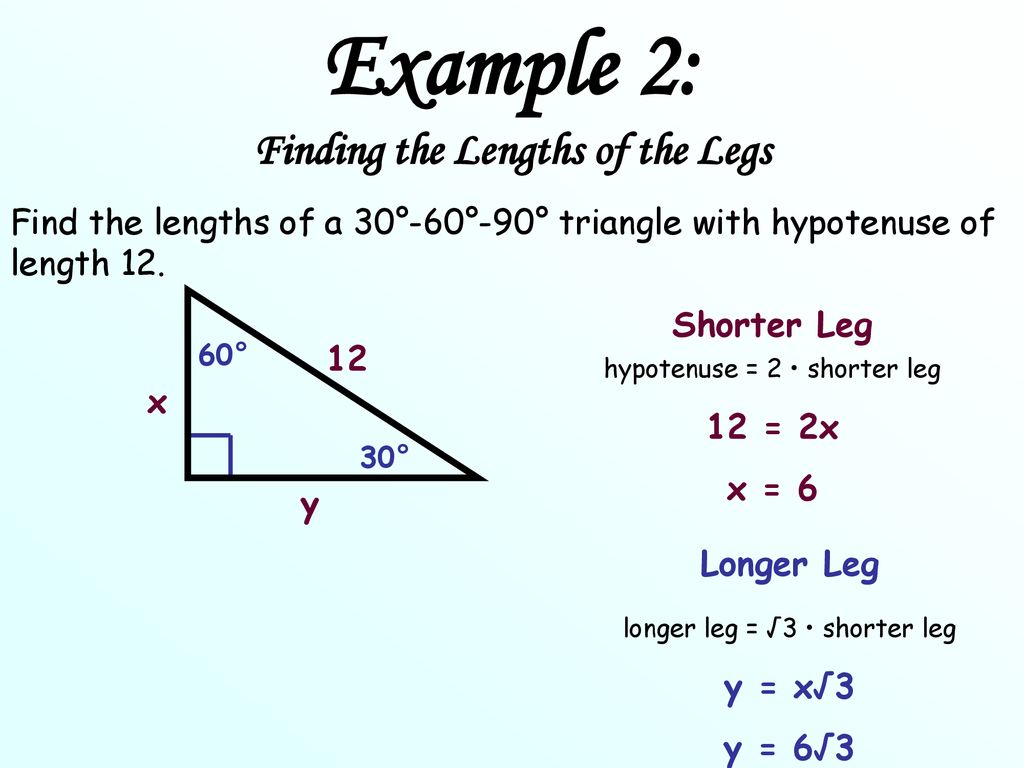



Objective To Use The Properties Of 30 60 90 Triangle Ppt Download
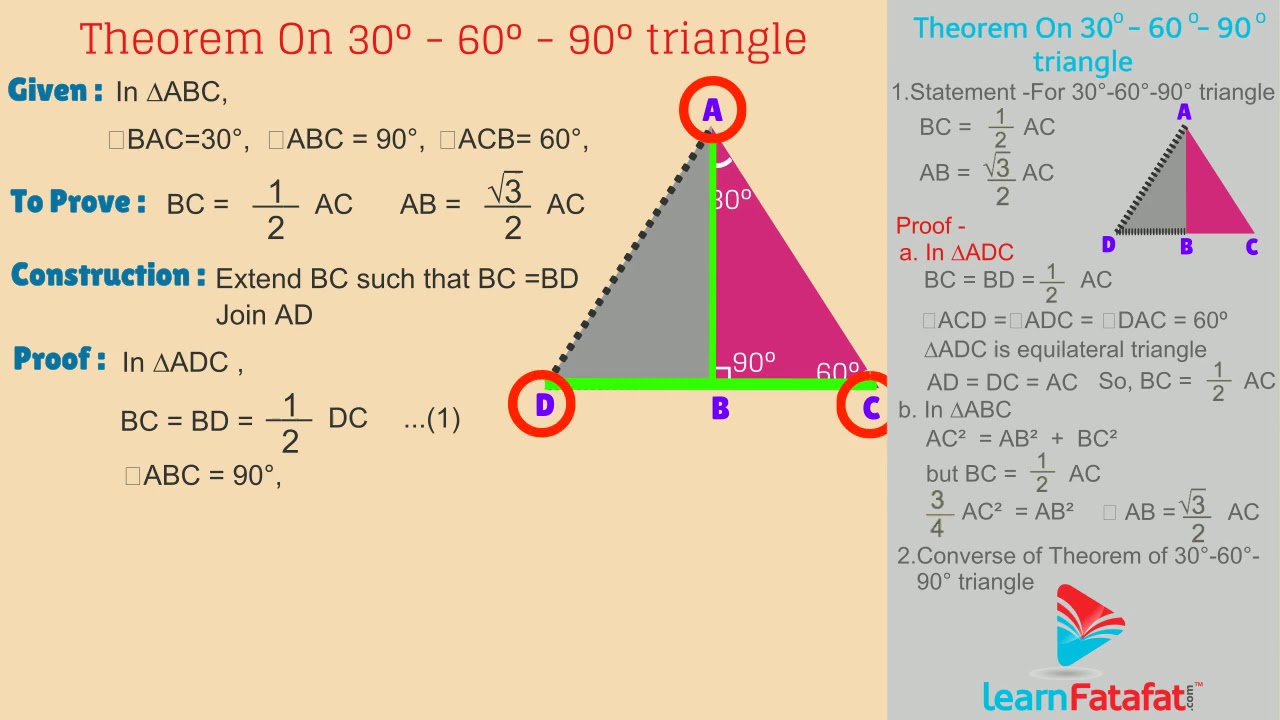
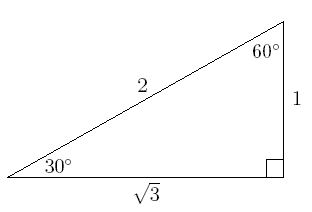
At a Glance Triangles The other magical right triangle comes from an equilateral triangle, or what might be better known as the Triforce from The Legend of Zelda Not one of those is a right triangle, but if we cut them in half, they will be Like the Gandalf triangle, knowing any side length of the Triforce triangle, which hasJustification The triangle was originally an equilateral triangle with three 60° angles The equilateral triangle was split down the middle, so α = 30° The other two angles on the side were not changed, so β = 60° Remember that the angles in a triangle must sum up to 180 ° Notice that 30° 60° 90° = 180° 1 cm cm 3 30° 60° 2 cmTHE 30°60°90° TRIANGLE THERE ARE TWO special triangles in trigonometry One is the 30°60°90° triangle The other is the isosceles right triangle They are special because, with simple geometry, we can know the ratios of their sides Theorem In a 30°60°90° triangle the sides are in the ratio 1 2 We will prove that below
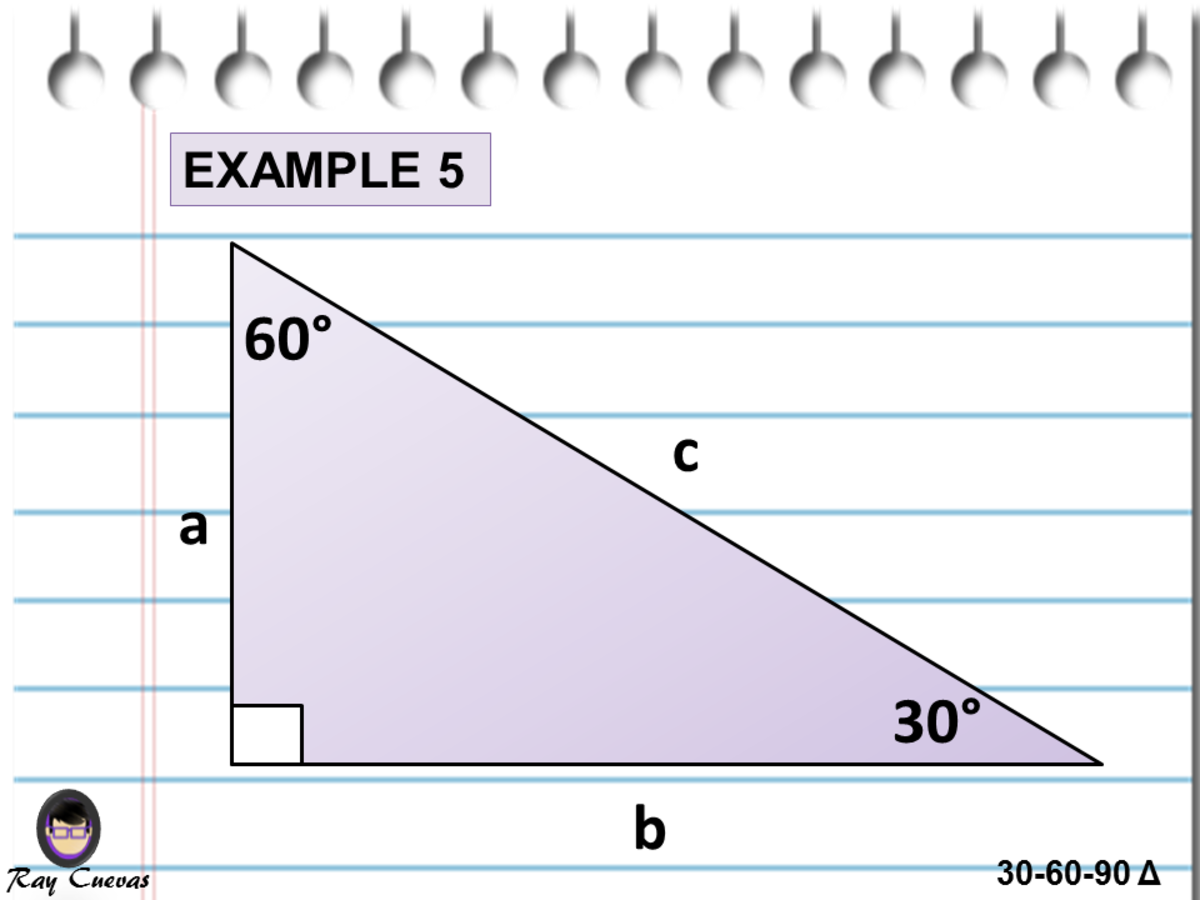



A Full Guide To The 30 60 90 Triangle With Formulas And Examples Owlcation




Solved Because A 30 60 Right Triangle Is Half Of An Chegg Com
The Triangle Inequality Theorem states that the sum of any 2 sides of a triangle must be greater than the measure of the third side Note This rule must be satisfied for all 3 conditions of the sides What is the formula for a 90 degree triangle?A triangle is a special right triangle with some very special characteristics If you have a degree triangle, you can find a missing side length without using the Pythagorean theorem!Question Problem 34 Use the facts about triangles (not the pythagorean theorem) to find the missing legs of each triangle Best well explained response gets 60 points
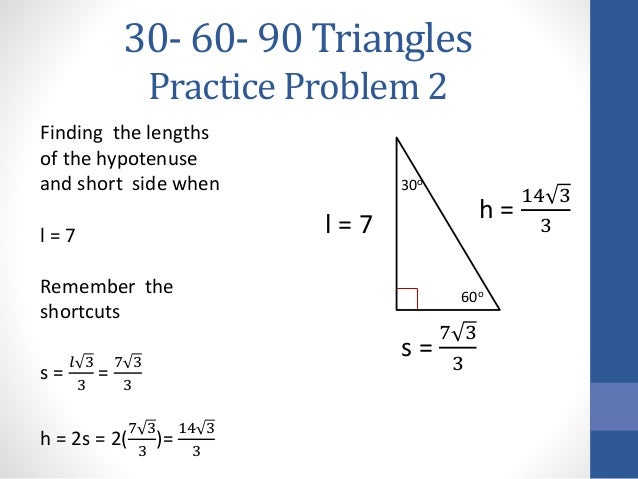



30 60 90 Triangles




30 60 90 45 45 90 Special Right Triangles Free Printable Math Worksheets Teaching Geometry Printable Math Worksheets
Triangles Page 4 of 5 The Shortcut The long leg is the same as the short leg times the square root of 3 This relationship is true of every triangle So from now on, don't use the Pythagorean Theorem Use the shortcut If you know the short leg, just multiply it by the square root of 3 to find the long leg Example 1 Find c and d Answer It might help to sketch outSee if you can divide the number by 4, 9, 16, 25, etc In this case, 25 is a perfect square that is a factor of 75 This means we can rewrite the problem as the square root of 25 times the square root of 3 The square root of 25 is 5, so this simplifies to 5 times the square root of 3 Now look at all three sides of the triangleTriangle in trigonometry In the study of trigonometry, the triangle is considered a special triangleKnowing the ratio of the sides of a triangle allows us to find the exact values of the three trigonometric functions sine, cosine, and tangent for the angles 30° and 60° For example, sin(30°), read as the sine of 30 degrees, is the ratio of the side



30 60 90 Triangle Definition Theorem Formula Examples




30 60 90 Triangle Theorem Properties Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
A 30°60°90° triangle is a right triangle that contains the acute angles 30° and 60° The sides of these triangles have lengths with special proportions We can obtain these proportions using the Pythagorean theorem For this, we can consider that the 30°60°90° triangle is half of an equilateral triangle as shown in the followingA triangle has the following side lengths AB = 12 unitsBC = 10 unitsAC = 16 units What type of triangle does this make?In the past, I have found it essential to emphasize the fact that the and triangles come from squares and equilateral triangles, respectively I reiterate to students that they must justify why the special right triangles rules work for all triangles and triangles—an algebraic argument or similar figures argument would suffice (for example, all




Special Right Triangles



Special Right Triangles Formulas 30 60 90 And 45 45 90 Special Right Triangles Examples Pictures And Practice Problems
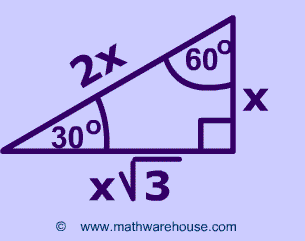
We can use the Pythagorean theorem to show that the ratio of sides work with the basic triangle above a2b2=c2 12(3–√)2=13=4=c2 4–√=2=c Using property 3, we know that all triangles are similar and their sides will be in the same ratio s #30 60 90 and 45 45 90 triangle #30 60 90 right triangle #30 60 90 A triangle is a right triangle with angle measures of 30º, 60º, and 90º (the right angle) Because the angles are always in that ratio, the sides are also always in the same ratio to each other The side opposite the 30º angle is the shortest and the length of it is usually labeled as x The side opposite the 60º angle has a30°60°90° Right Triangles All 30°60°90° Right Triangles are formed by taking half of a Equilateral Triange, as shown in the steps below Because the original triangle is Equilateral, that means all three sides are the same length This is what variable "x" is trying to tell you All three sides are the same length Therefore, looking at diagram two, when you cut the triangle in half



Pythagoras Theorem On 30 60 90 Triangle Youtube



Special Right Triangles Fully Explained W 19 Examples
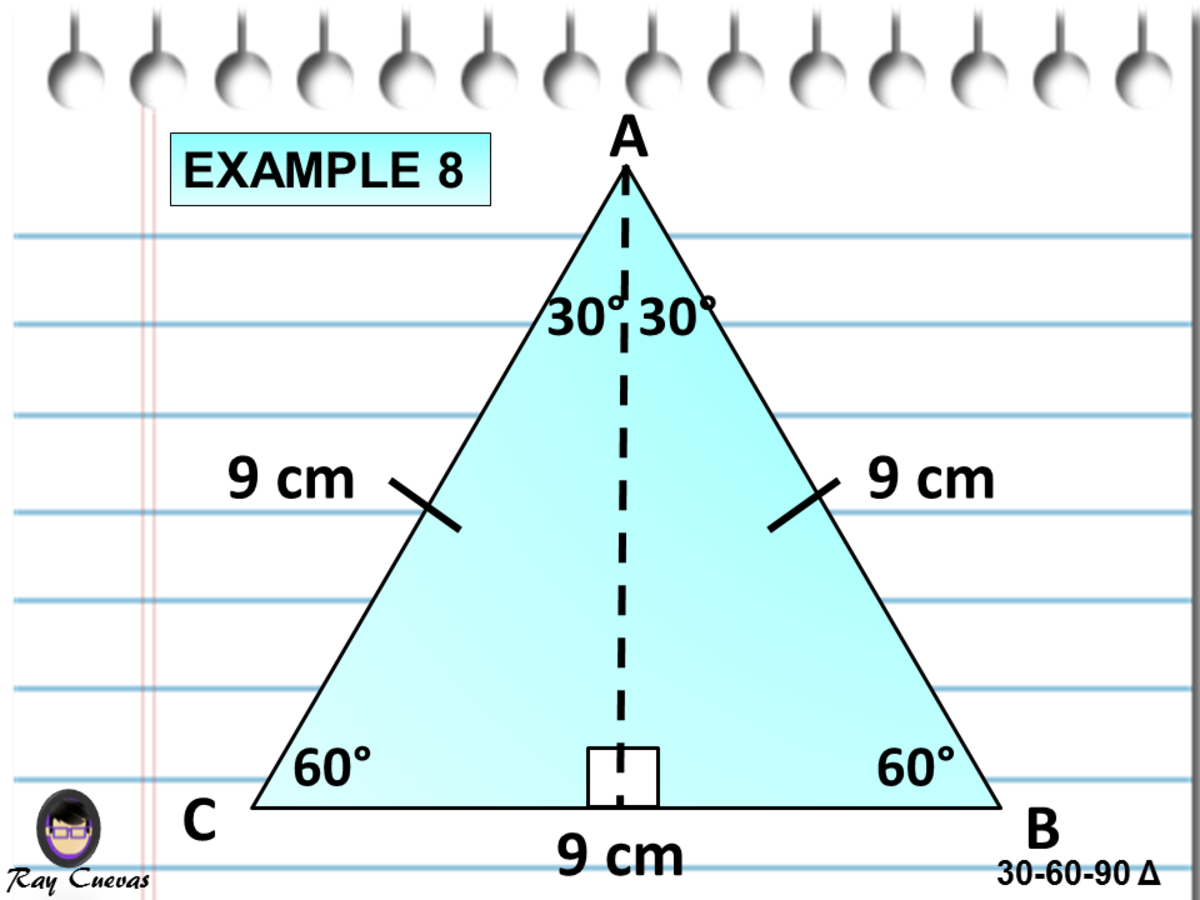
The 30 60 90 triangle is special because it forms an equilateral triangle when a mirror image of itself is drawn, meaning all sides are equal!
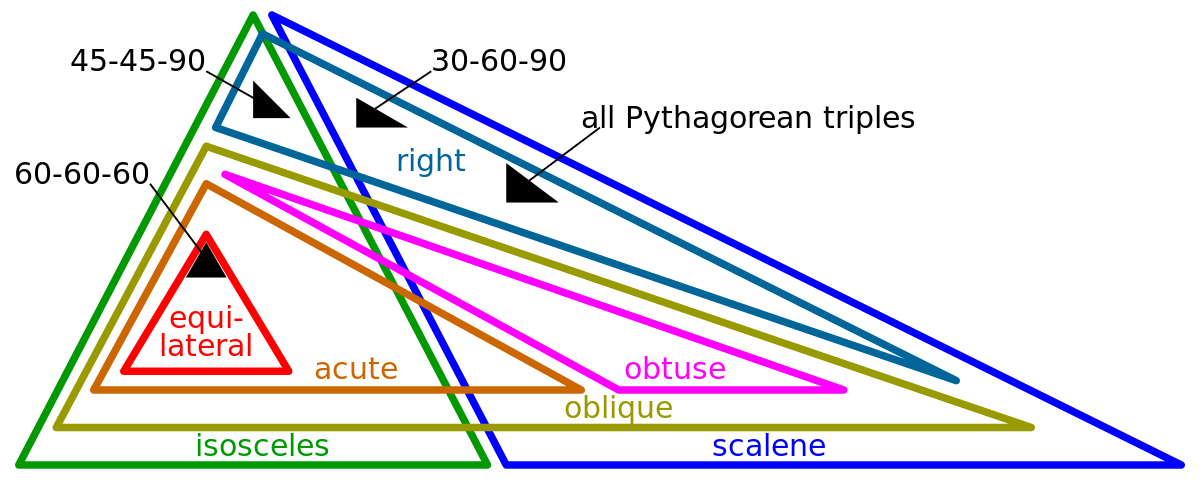



Special Right Triangle Wikipedia




30 60 90 Right Triangles Ck 12 Foundation



30 60 90 Triangle Formulas Rules And Sides Science Trends




30 60 Degree Right Triangles Pythagoras Theorem 630x361 Png Download Pngkit




30 60 90 Triangle Theorem Ratio Formula Video
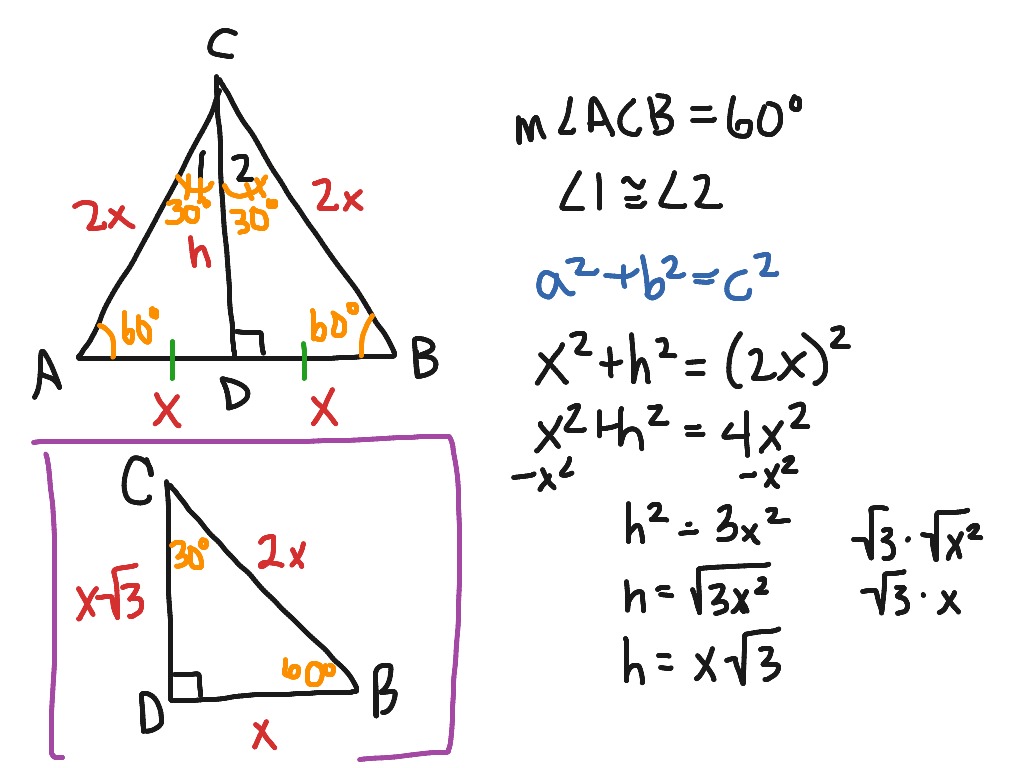



30 60 90 Triangle Math Right Triangles Showme



Geometry Pythagorean Theorem Special Right Triangles Scavenger Hunt
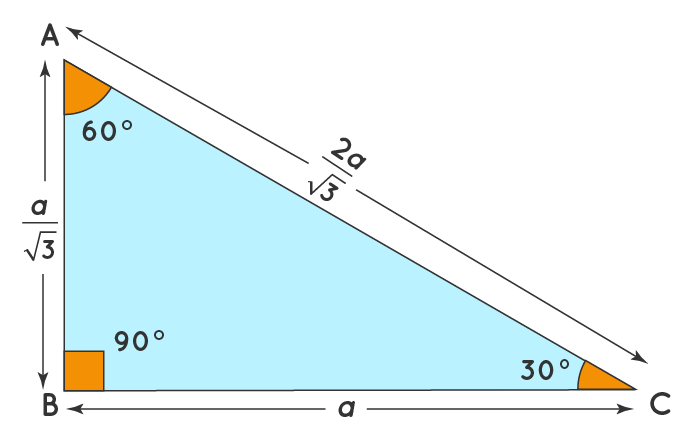



30 60 90 Triangle Definition Theorem Formula Examples
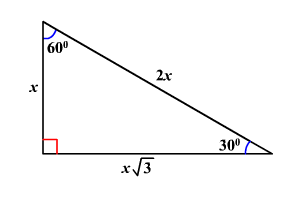



30 60 90 Triangles



Pythagorean Triples
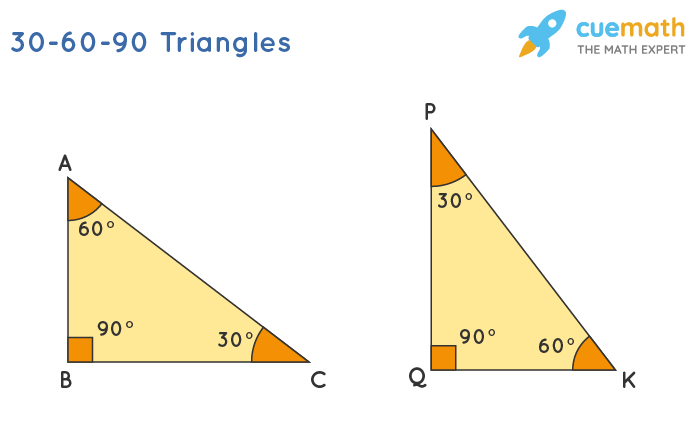



30 60 90 Triangle Definition Theorem Formula Examples




30 60 90 Triangle Theorem Ratio Formula Video




30 60 90 Triangle Theorem Ratio Formula Video
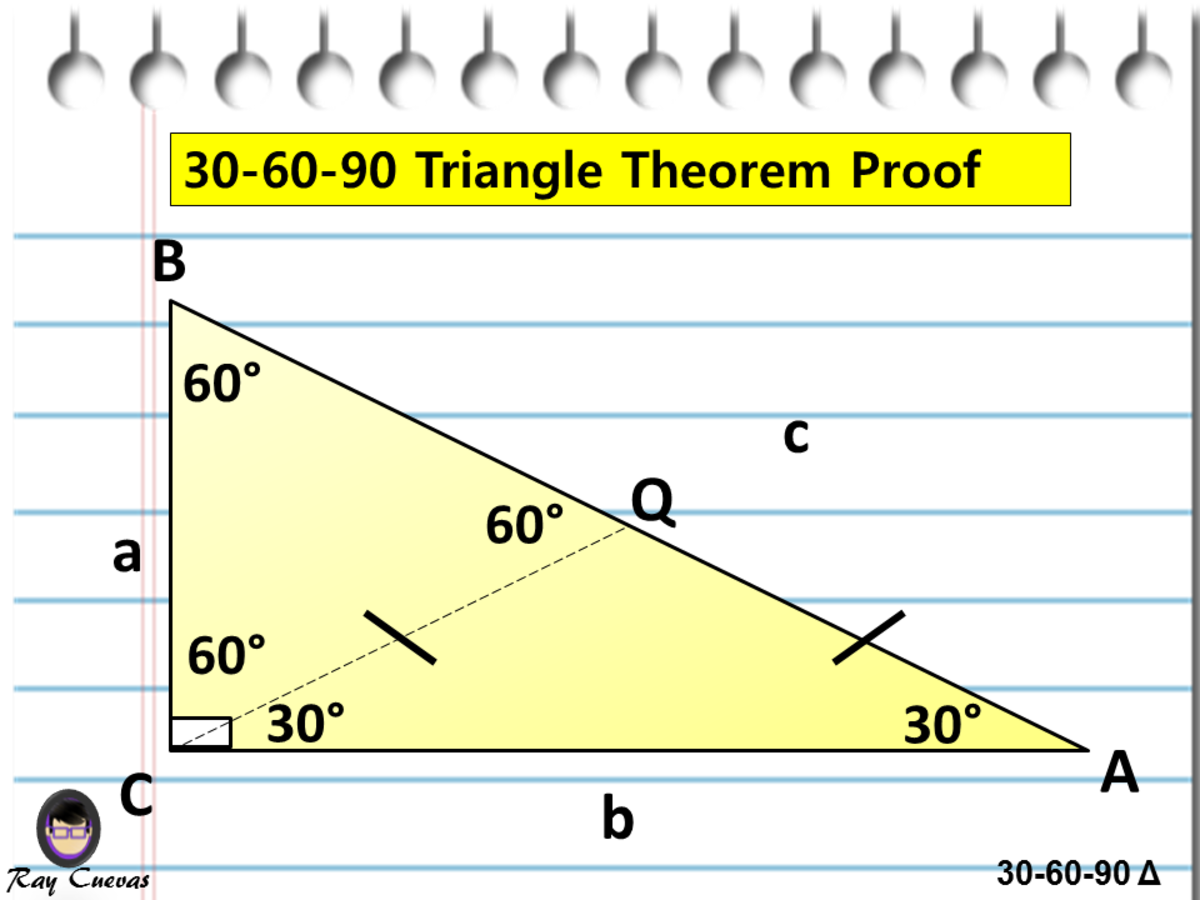



A Full Guide To The 30 60 90 Triangle With Formulas And Examples Owlcation




30 60 90 Triangle Theorem Properties Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



A Full Guide To The 30 60 90 Triangle With Formulas And Examples Owlcation



How To Use The Special Right Triangle 30 60 90 Studypug




30 60 90 Triangle Calculator Formula Rules




30 60 90 Triangle Theorem Ratio Formula Video




30 60 90 Triangle Theorem Properties Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Precalculus 4 3 Right Triangle Trigonometry 1 The




30 60 90 Triangle Theorem Proof Don T Memorise Youtube



The Length Of The Hypotenuse Of A 30 60 90 Triangle Is 12cm What Is The Length Of The Longer Leg What Is The Length Of The Shorter Leg Quora



The Easy Guide To The 30 60 90 Triangle



Precalculus Notes Trig 3




Right Triangles And Pythagorean Theorem My Act Guide



30 60 90 Triangle Geometry Help



1



Special Right Triangles Review Article Khan Academy




30 60 90 Triangles Concept Trigonometry Video By Brightstorm
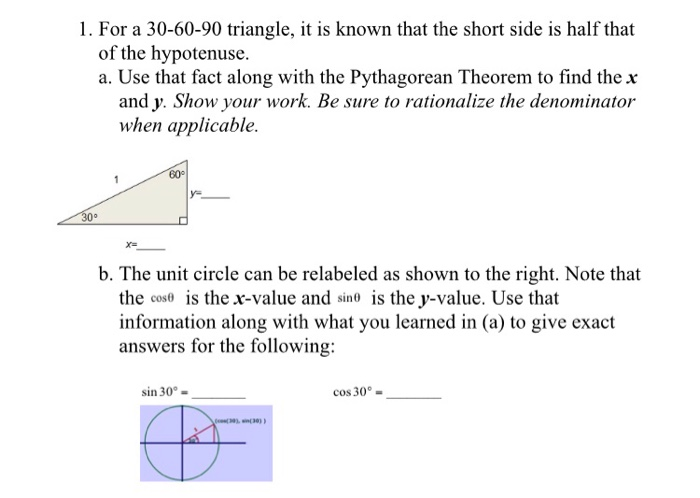



Solved 1 For A 30 60 90 Triangle It Is Known That The Chegg Com



Trigonometry
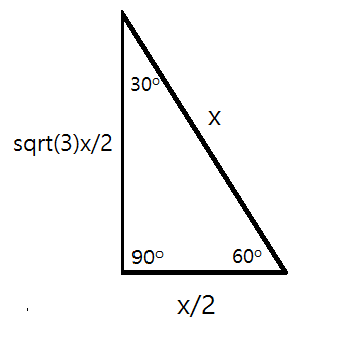



What Is A 30 60 90 Triangle Please Give An Example Socratic
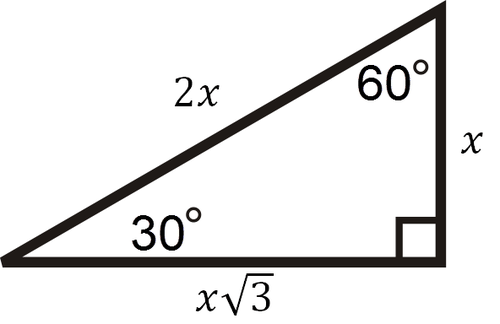



Special Right Triangles Read Geometry Ck 12 Foundation



30 60 90 Triangle Rules




30 60 90 Triangle Theorem Ratio Formula Video
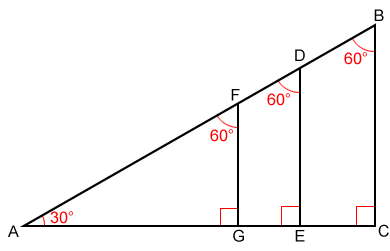



30 60 90 Triangle
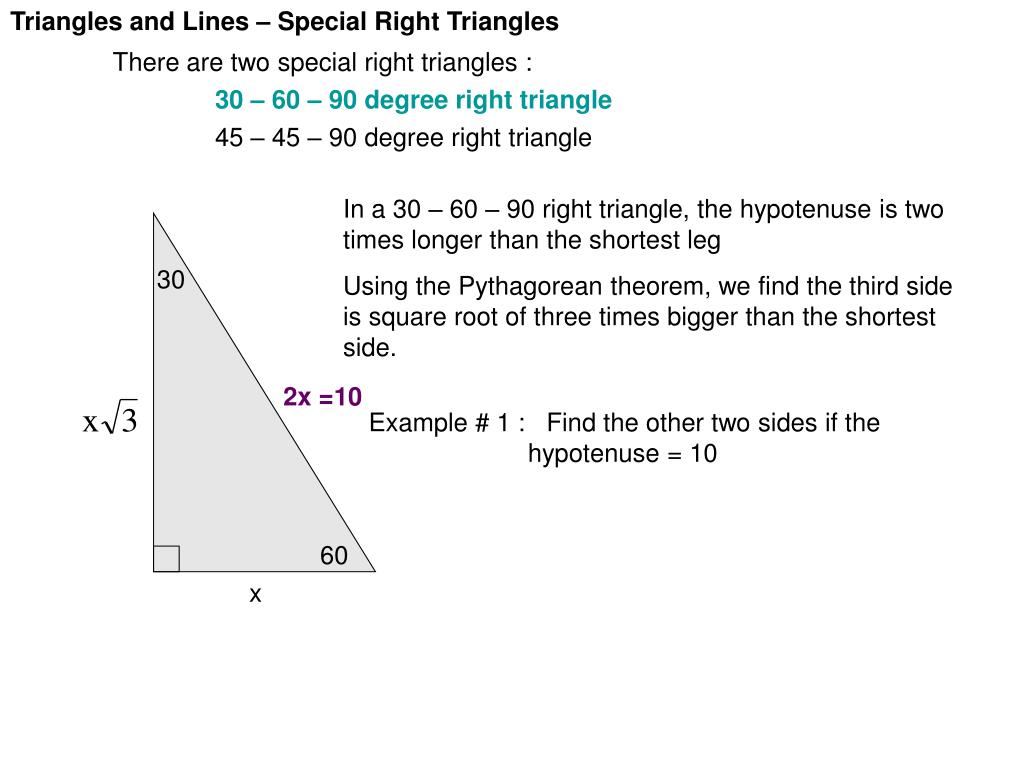



Ppt Triangles And Lines Special Right Triangles There Are Two Special Right Triangles Powerpoint Presentation Id




Pythagoras Theorem Class 10 Chapter 2 Part 1 Pythagorean Theorem 30 60 90 Triangle Youtube
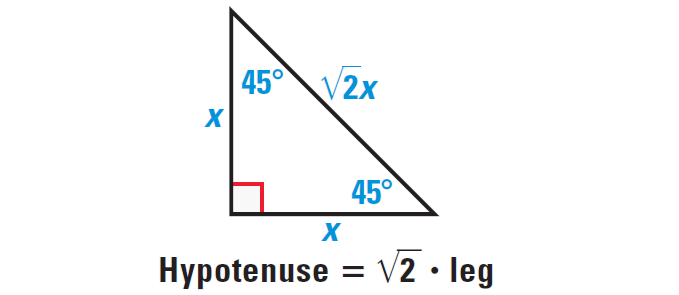



Theorems About Special Right Triangles




30 60 90 Triangle Explanation Examples



Special Right Triangles
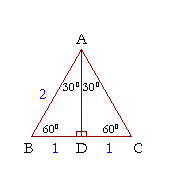



30 60 90 Right Triangle Side Ratios Expii



Special Right Triangle 30 60 90 Mathbitsnotebook Geo Ccss Math




30 60 90 Special Triangles Geometry Mathsux 2
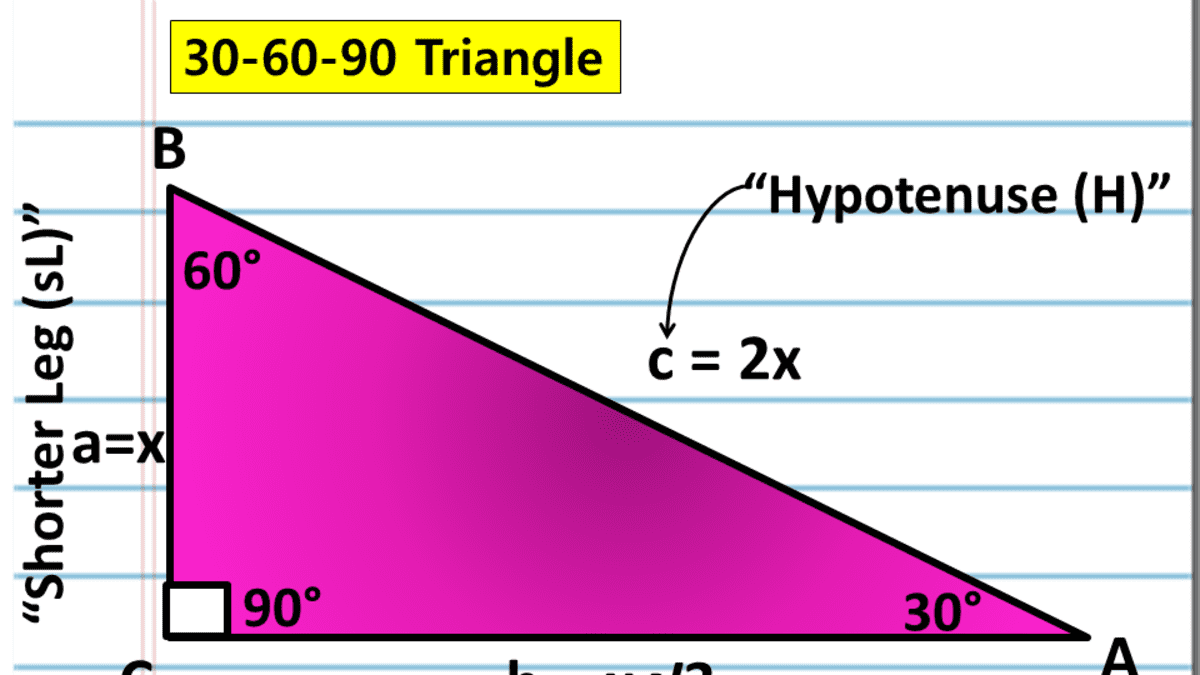



A Full Guide To The 30 60 90 Triangle With Formulas And Examples Owlcation




How To Solve 30 60 90 Triangle Problems Educational Star
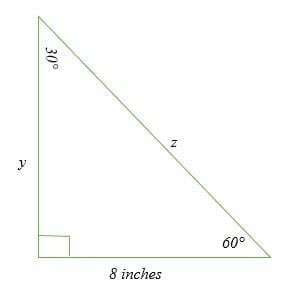



30 60 90 Triangle Explanation Examples
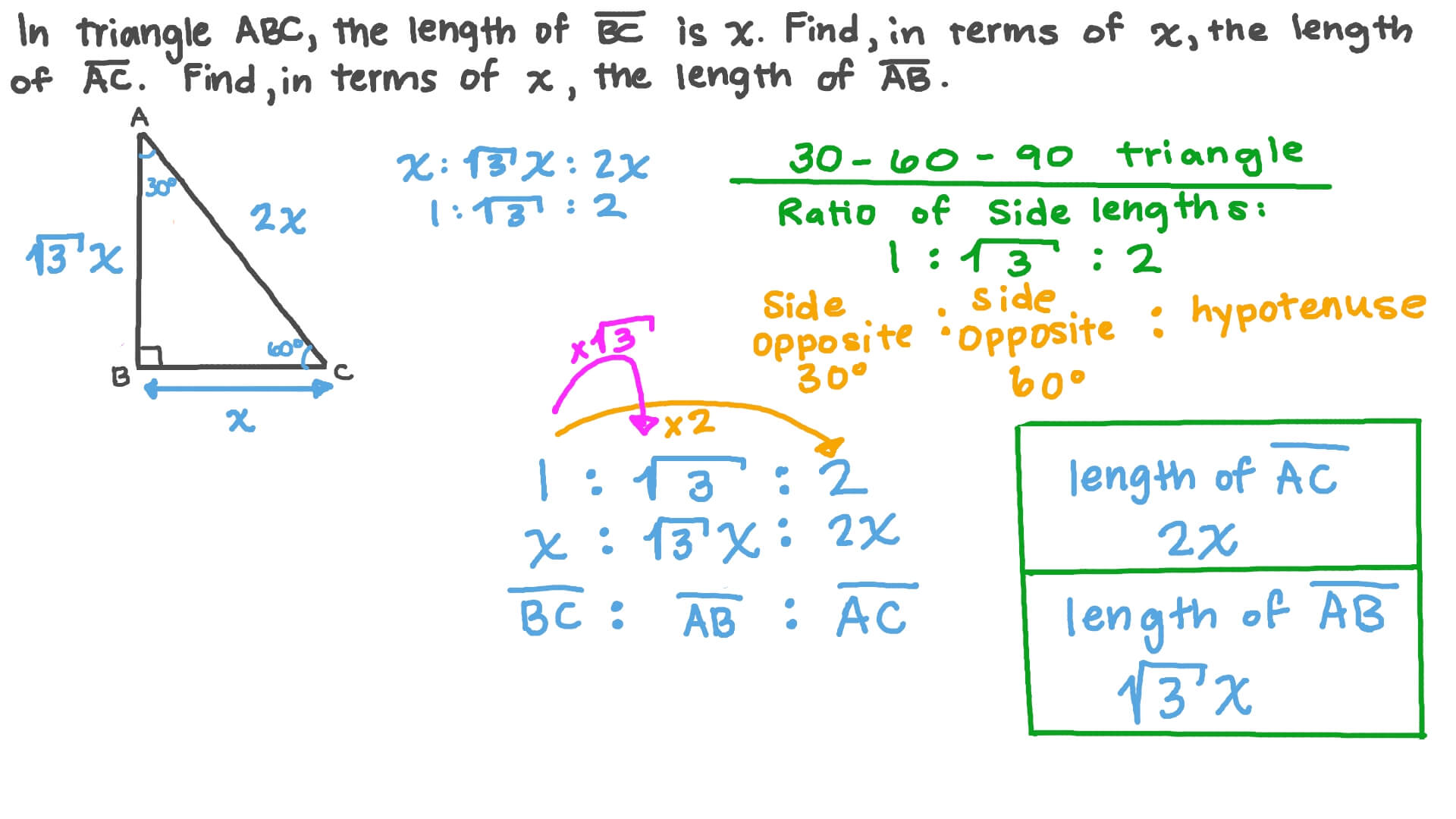



Question Video The Side Lengths Of 30 60 90 Triangles Nagwa
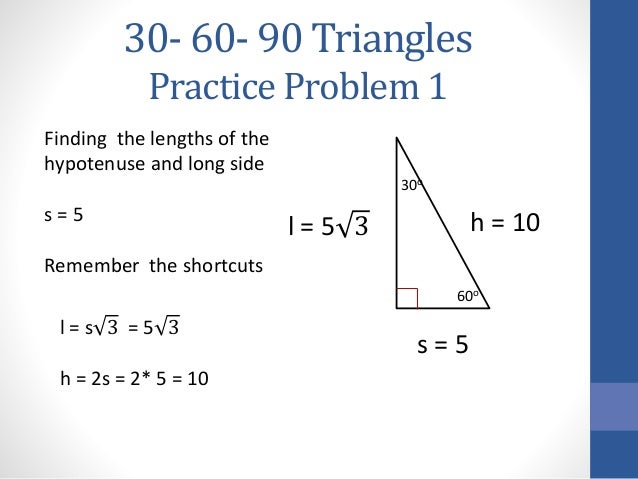



30 60 90 Triangles




30 60 90 Triangle Calculator Formula Rules
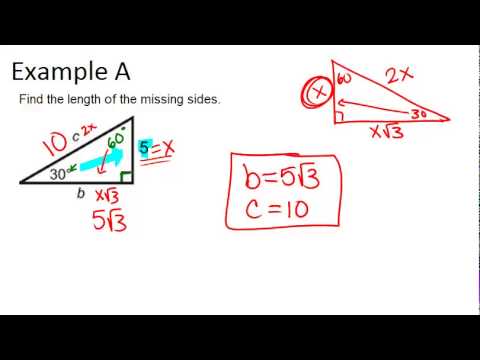



30 60 90 Right Triangles Examples Geometry Concepts Youtube



Special Right Triangles Proof Part 1 Video Khan Academy



The Converse Of The Pythagorean Theorem And Special Triangles Geometry Right Triangles And Trigonometry Mathplanet




30 60 90 Triangles Free Math Lessons Geometry Lessons Printable Study Guides



5 5 Special Triangles



What Are The Side Ratios For A 30 60 90 Triangle Quora



30 60 90 Right Triangles Solutions Examples Videos



9th Maths 2 30 60 90 Triangle Theorem Youtube
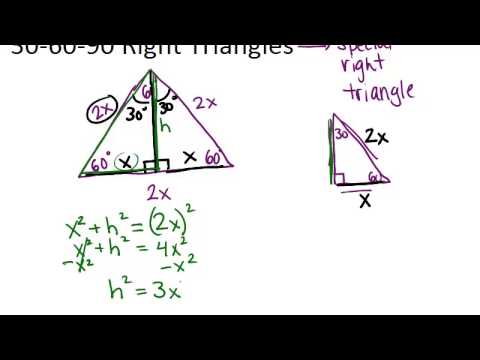



30 60 90 Right Triangles Lesson Geometry Concepts Youtube




Special Right Triangles Proof Part 1 Video Khan Academy
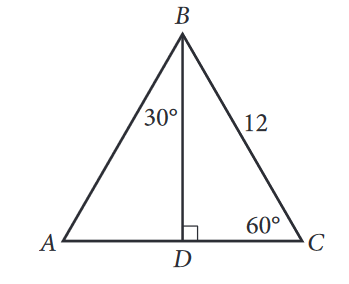



The Complete Guide To The 30 60 90 Triangle




5 30 60 90 Triangles Geometry15a
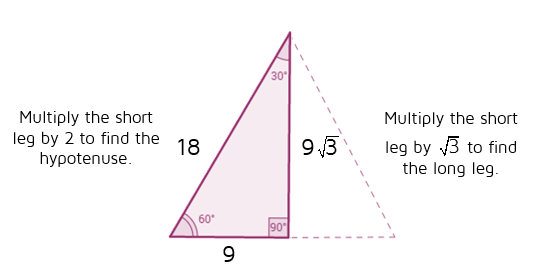



30 60 90 Triangles P4 Kate S Math Lessons



1




Mrs Newell S Math Better Questions Special Right Triangles
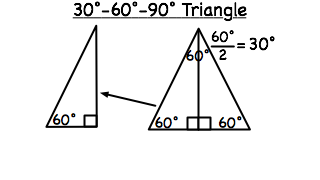



What Is A 30 60 90 Degree Triangle Virtual Nerd Can Help




Learn About The 30 60 90 Triangle Caddell Prep Online
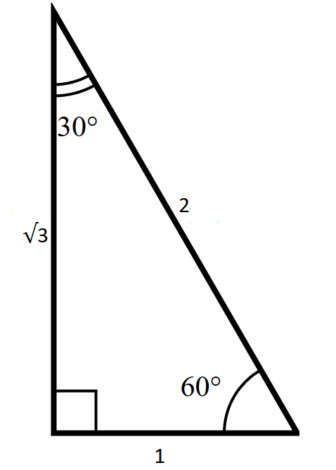



The Complete Guide To The 30 60 90 Triangle
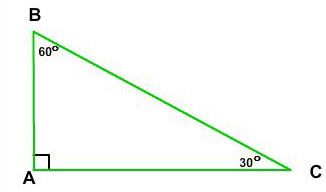



30 60 90 Right Triangle Side Ratios Expii




30 60 90 Triangle Sides Examples Angles Full Lesson




30 60 90 Triangle Theorem Properties Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Special Right Triangles Proof




30 60 90 Triangle Theorem Ratio Formula Video



The Easy Guide To The 30 60 90 Triangle




Use Pythagorean Theorem X 12 7 Rounded This Is A Triangle On A Sheet Of Paper Ppt Download



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿